Arthritis, a term encompassing a group of disorders that result in joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness, has long been a challenge for millions worldwide. Its multifaceted impact on individuals spans from daily discomforts to significant lifestyle changes. As medical technology and understanding of cellular processes advance, innovative therapies emerge, offering renewed hope.
One such promising avenue is Red Light Therapy (RLT). While the name may evoke simplicity, the underlying physiological mechanisms are intricate and deeply rooted in our cells’ foundational biochemistry. This article will delve into the molecular ballet that unfolds when red light interacts with our tissues, and how this dance might hold the key to alleviating some of the burdens arthritis patients bear daily.
Benefits of Red Light Therapy for Arthritis
The intersection of Red Light Therapy (RLT) and arthritis is a confluence of hope and science. As we unravel the multifaceted biological interactions of RLT, its benefits, especially for those burdened by arthritis, become more evident. Here are some of the notable advantages derived from the physiological mechanisms of action:
PAIN REDUCTION CAUSED BY ARTHRITIS
Pain, a constant companion of arthritis sufferers, can be debilitating. RLT, by stimulating the mitochondria and optimizing ATP production, aids in cellular repair processes. This cellular rejuvenation, coupled with the modulation of certain neural pathways and the reduction of inflammatory mediators, contributes to a tangible alleviation of pain. Clinical studies have often showcased patients reporting significant pain relief post-RLT sessions.
IMPROVED MOBILITY TO RED LIGHT THERAPY
The anti-inflammatory effects of RLT are not just confined to pain reduction. By curtailing the inflammatory cascade, there’s reduced joint swelling and stiffness. This, in turn, can lead to an enhanced range of motion, allowing arthritis patients to regain some of the mobility they might have lost due to their condition.
REDUCED MEDICATION FOR ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
The holistic nature of RLT’s biological interactions means that some patients might find a decrease in their dependency on medications, especially pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. By addressing the root causes, inflammation and cellular dysfunction, RLT can potentially reduce the symptoms, thereby decreasing the need for symptom-alleviating medications.
SAFETY OF RED LIGHT THERAPY
One of the standout attributes of RLT is its safety profile. Being a non-invasive therapy, it circumvents many of the side effects associated with oral medications or more invasive procedures. While every therapy has its considerations, RLT’s side-effect profile is minimal, especially when protocols are adhered to properly.
In a landscape often dominated by potent medications with their side-effect specters, RLT emerges as a beacon of therapeutic potential. By tapping into the body’s intrinsic cellular mechanisms, it offers a reprieve to those seeking relief from the relentless grasp of arthritis.
The Science Behind Red Light Therapy for Arthritis
Peeling back the layers of Red Light Therapy reveals an intricate web of biological processes. When applied to the context of arthritis, RLT’s influence becomes even more intriguing. Let’s unpack the physiological dance that transpires when red light meets our bodily tissues:
PHOTON ABSORPTION FOLLOWING RED LIGHT THERAPY
Our body’s cells, especially those in the skin and subcutaneous layers, have the ability to absorb photons emanating from the red light. This absorption is not a passive process; it’s the beginning of a cellular symphony. When these photons are absorbed, they interact with the mitochondria, the cellular organelles often described as the energy factories of our cells.
CYTOCHROME C OXIDASE STIMULATION
Within the mitochondria, an enzyme called cytochrome c oxidase plays a pivotal role in the respiratory chain – a sequence of reactions that culminates in the production of ATP. RLT’s wavelengths specifically stimulate cytochrome c oxidase, enhancing its activity.
ENHANCED ATP PRODUCTION
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often labeled the ‘energy currency’ of the cell. With the stimulation of cytochrome c oxidase, there’s a surge in ATP production. An abundance of this molecule means that cells have more energy at their disposal for repair, regeneration, and carrying out their specialized functions.
REDUCED INFLAMMATION
Inflammation is a hallmark of arthritis. Intriguingly, RLT influences the inflammatory pathway at the molecular level. It reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, signaling proteins that exacerbate inflammation, while simultaneously increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. This delicate balance shifts the inflammatory response towards a state of resolution rather than perpetuation.
Through these interconnected processes, RLT offers a unique therapeutic modality. Its ability to penetrate deeply and influence cellular mechanisms makes it a compelling option for those grappling with the multifaceted challenges of arthritis.
What is Red Light Therapy?
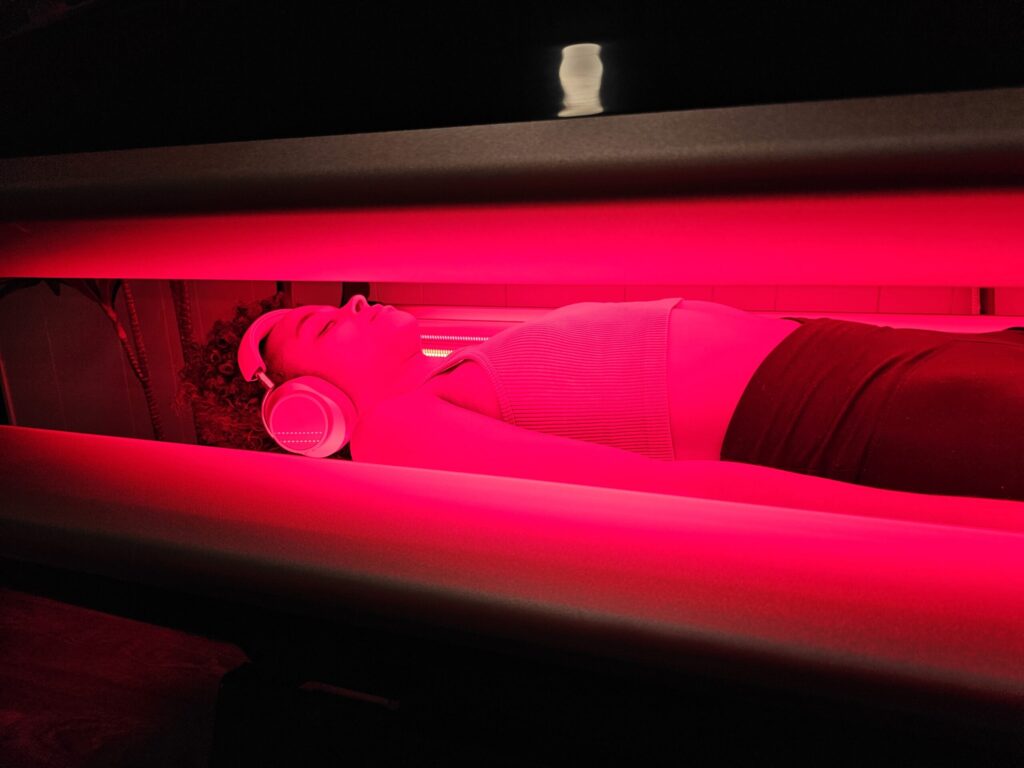

Red Light Therapy (RLT) is a cutting-edge approach that harnesses specific wavelengths of light to interact with human tissue. Predominantly, this involves wavelengths in the red to near-infrared spectrum (approximately 600 to 1100 nanometers). While superficially it might seem like just another light source, the potency of RLT stems from its ability to penetrate the skin and other biological tissues, instigating a cascade of cellular responses.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RED LIGHT THERAPY AND OTHER TYPES OF THERAPIES
It’s crucial to differentiate RLT from other forms of light therapies. For instance:
Blue Light Therapy
This operates at shorter wavelengths (around 400-495 nm) and is primarily used for acne management, skin cancer, mood disorders, and circadian rhythm adjustment.
Ultraviolet (UV) Light
A shorter wavelength light that, in controlled doses, can help conditions like psoriasis, but it has its share of risks, including the potential for skin cancer.
So, what makes RLT stand out? At the cellular level, RLT’s specific wavelengths stimulate mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells. By influencing the mitochondrial enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, RLT boosts the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – our cells’ primary energy currency. This elevation in ATP, coupled with other biological reactions, triggers a host of benefits that may prove invaluable for arthritis sufferers.
Clinical Studies and Evidence of Red Light Therapy
The strong interest in Red Light Therapy (RLT), or Photobiomodulation (PBM) as it’s scientifically termed, for arthritis management is not just anecdotal. A growing body of research underscores its potential, shedding light on the intricate cellular mechanisms at play and providing empirical evidence of its therapeutic benefits. Here’s a brief review of some pivotal studies in the domain:
THE POTENTIAL OF RED LIGHT THERAPY
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Arthritis in Children and Adults: New Perspectives on Applied Photobiomodulation
This comprehensive study delved into the intricacies of arthritis, particularly examining the cellular dynamics in both pediatric and adult populations. A standout finding from this research is the quote:
“Applied PBM could be a safe and an exceptionally good option in the multidisciplinary management of rheumatoid arthritis and chronic pain in children and adults.”[1]
Such a statement underscores the potential of RLT in providing relief across a wide age spectrum, emphasizing its versatility and safety.
BUILDING A STRONG FOUNDATION FOR ARTHRITIS TREATMENT
Photobiomodulation effects in metalloproteinases expression in zymosan-induced arthritis
Metalloproteinases are enzymes implicated in the breakdown of extracellular matrix, playing a pivotal role in inflammatory conditions like arthritis. This study shed light on how PBM interacts with these enzymes, influencing their expression and activity. The authors noted:
“PBM promotes a better arthritis prognostic, modulating metalloproteinase and its inhibitor, especially MMP-9 and TIMP-2 protein expression that are important inflammatory markers.”[2]
The modulation of these key proteins provides a molecular rationale for the therapeutic benefits observed in arthritis patients undergoing RLT.
The Mechanisms and Efficacy of Photobiomodulation Therapy for Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review
This exhaustive review casts a wide net, capturing the multifarious ways in which PBM interacts with the arthritic milieu. From cellular signaling pathways to clinical outcomes, the review provides a panoramic view of RLT’s potential. A salient takeaway from this research is:
“PBM therapy shows great promise as an effective and non-invasive therapy for arthritis.”[3]
Such a statement, backed by a compendium of evidence, bolsters the case for integrating RLT into the arsenal of arthritis management strategies.
These studies, among others, lay a solid foundation for the burgeoning enthusiasm around Red Light Therapy. With a synthesis of molecular insights and clinical outcomes, they offer a beacon of hope for those grappling with the complexities of arthritis.
Specific Wavelengths of Red Light Therapy for Arthritis
Within the spectrum of Red Light Therapy (RLT), not all wavelengths are created equal. Specific wavelengths have been identified as particularly potent for addressing the challenges posed by arthritis. The precision of these wavelengths allows for targeted interactions with biological tissues, optimizing the therapeutic outcomes. Let’s delve into the nuances of these select wavelengths.
630NM
This wavelength, situated in the red light spectrum, is adept at penetrating the skin’s superficial layers. Its interaction with cellular components, particularly the mitochondria, facilitates enhanced adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. This boosts cellular energy, aiding in repair and regeneration processes that are crucial for arthritis-affected regions.
660NM
Closely following the previous wavelength, 660nm has demonstrated efficacy in modulating inflammatory pathways. By influencing the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, it assists in reducing joint inflammation, a cardinal symptom of arthritis.
830NM
Venturing into the near-infrared spectrum, this wavelength penetrates deeper into the body’s tissues. Their depth of penetration allows it to influence not just skin and subcutaneous layers but also deeper musculoskeletal structures. This depth is particularly valuable for addressing arthritis symptoms in larger joints.
The choice of specific wavelengths isn’t arbitrary. Backed by scientific studies and a deep understanding of cellular physiology, these wavelengths are chosen for their ability to target the root causes of arthritis symptoms. Integrating RLT into the management strategy for arthritis, with a focus on these particular wavelengths, provides a science-backed approach that taps into the body’s intrinsic healing mechanisms.
Red Light Therapy For Arthritis Summary
Red Light Therapy (RLT), with its intricate interplay of wavelengths and cellular mechanisms, emerges as a beacon of therapeutic potential for those battling the challenges of arthritis. Harnessing specific wavelengths – namely 630nm and 830nm – RLT offers a symphony of physiological responses that address the multifaceted manifestations of arthritis.
From stimulating mitochondria and optimizing ATP production to modulating inflammatory pathways and enhancing circulation, the therapeutic tapestry of RLT is vast. By acting on these foundational biological processes, RLT transcends merely alleviating symptoms; it interacts with the very molecular dynamics underpinning arthritis.
As the realm of medical science continually evolves, the fusion of empirical evidence and our growing understanding of cellular processes positions Red Light Therapy as a formidable contender in the holistic management of arthritis. While it’s essential to approach every therapy judiciously and in collaboration with healthcare professionals, the scientific community’s growing recognition of RLT’s merits offers hope and a promising avenue for those seeking relief.
Article References
[1] Ailioaie LM, Litscher G. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Arthritis in Children and Adults: New Perspectives on Applied Photobiomodulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 8;21(18):6565. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186565. PMID: 32911717; PMCID: PMC7554967.
[2] Dos Anjos LMJ, Quirino-Teixeira AC, Hottz ED, da Fonseca AS, Gameiro J, de Paoli F. Photobiomodulation effects in metalloproteinases expression in zymosan-induced arthritis. Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Dec;37(9):3661-3670. doi: 10.1007/s10103-022-03647-4. Epub 2022 Sep 26. PMID: 36156751.
[3] Zhang R, Qu J. The Mechanisms and Efficacy of Photobiomodulation Therapy for Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 19;24(18):14293. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814293. PMID: 37762594; PMCID: PMC10531845